Polyethylene (PE): The World’s Most Common Plastic
Polyethylene (PE) often abbreviated as PE, is a widely used, versatile thermoplastic polymer made from ethylene monomers. From polyethylene panels to polyethylene piping, and from food packaging to industrial tanks, PE materials are found everywhere.
The Monomer and Polymerization
The fundamental building block is the ethylene monomer (C₂H4), a simple gas derived primarily from crude oil or natural gas.
- Monomer: Ethylene (C₂H4) has the chemical structure CH₂=CH₂.
- Polymerization: How is polyethylene manufactured? The process, known as polyethylene polymerization, involves using heat, pressure, and catalysts to link thousands of ethylene monomers together. This forms long molecular chains.
- Structure: The resulting polyethylene structure (or polyethylene chemical structure) is a straight chain of carbon atoms with two hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon: (–CH₂–CH₂–)_n$. The PE chemistry is fundamentally simple, lacking complex side groups. The molar mass of polyethylene (or polyethylene molar mass) is not fixed but can range from thousands to millions of grams per mole, depending on the grade.
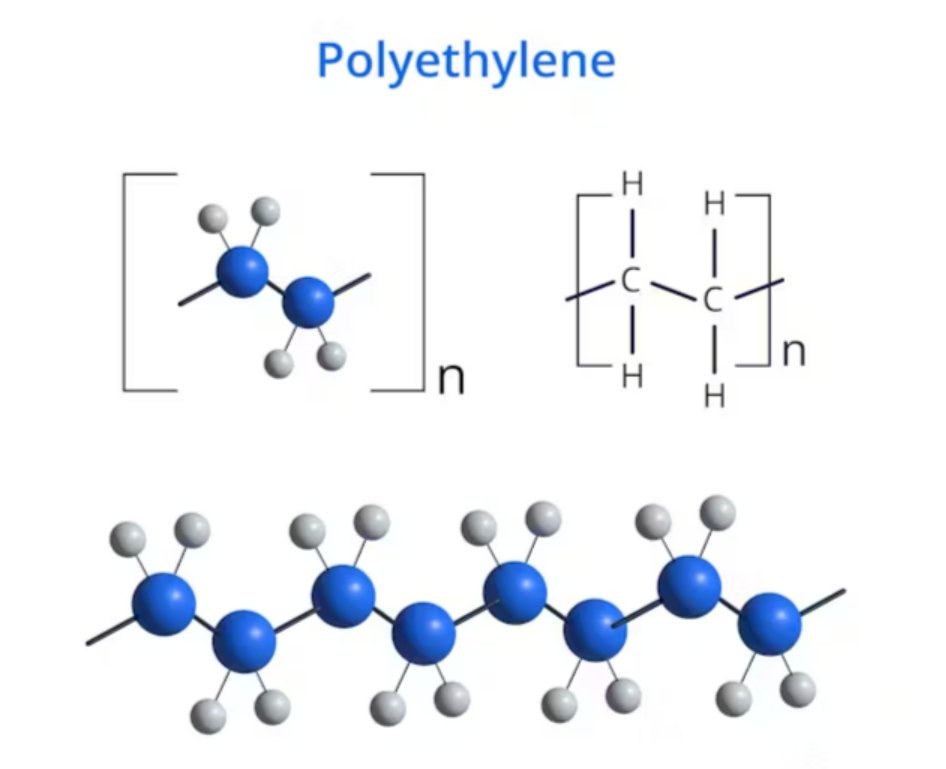
The Science: Is Polyethylene a Polymer or a Plastic?
The short answer is: both.
- Polymer: Polyethylene is first and foremost a polymer. This means it is a large molecule formed by the repetition of smaller, identical units called monomers. In the case of Polyethylene, the monomer is ethylene (a simple hydrocarbon gas). The process of chaining these molecules together is called polymerization. The Polyethylene chemical structure consists of long chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
- Plastic: Because Polyethylene is an organic polymer that can be shaped (molded or extruded) when heated, it is classified as a plastic.

Key Types and Properties of Polyethylene
polyethylene grades
The key to polyethylene’s versatility lies in its various types of polyethylene (or polyethylene grades), which differ primarily in molecular weight, branching, and density of PE.
| PE Grade | Abbreviation | Branching | PE Density (g/cm³) | PE Melting Point (∘C) | Key Uses |
| High-Density PE | HDPE | Minimal | 0.941 – 0.965 | 120 – 135 | Rigid containers (bottles, drums), pipe systems (polyethylene piping). |
| Low-Density PE | LDPE | High, short-chain | 0.910 – 0.940 | 105 – 115(LDPE melting temperature) | Polyethylene film (plastic bags, shrink wrap), flexible lids. |
| Linear Low-Density PE | LLDPE | Minimal, short co-monomer branches | 0.915 – 0.925 | 118 – 125(Linear low density polyethylene melting point) | Stretch film, heavy-duty bags, tougher films. |
| Medium-Density PE | MDPE | Moderate | 0.926 – 0.940 | 120 – 130 | Gas pipes, fittings, packaging film. |
Polyethylene Properties
- Polyethylene Density: The polyethylene density is a critical factor determining the material’s stiffness, strength, and crystallinity.
- Chemical Resistance: Excellent resistance to acids, bases, and general solvents.
- Safety: most pure grades of PE plastic are considered food safe and are widely used in food packaging.
- Processability: It is easy to process via extrusion (for polyethylene film and pipe) and molding, and is excellent for polyethylene welding.
Applications and Uses
The material’s low cost, resistance to moisture, and flexibility mean that polyethylene uses span consumer and industrial markets.
| Polyethylene Products | PE Type | Description |
| Packaging Films | LDPE, LLDPE | Plastic shopping bags, food wrap, shrink wrap. |
| Piping Systems | HDPE, MDPE | Gas distribution lines, water mains (1.5 inch polyethylene pipe), drainage pipes. |
| Containers | HDPE | Milk jugs, detergent bottles, storage containers. |
| Panels | HDPE | Polyethylene panels for playground equipment, cutting boards. |
| Tanks/Storage | HDPE | Large chemical or water storage tanks. |