What Is Polypropylene?
Polypropylene (PP), also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications. It is produced via chain-growth polymerization from the monomer propylene. It is one of the most commonly produced propylene polymers, known for excellent chemical resistance, low density, high fatigue strength, and cost-effectiveness.
Chemical Structure of PP
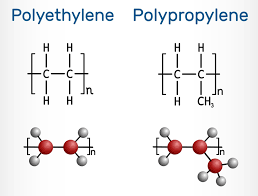
PP structure is based on the propylene monomer (C₃H6).
- Monomer: Propylene (CH₂=CH(CH₃)).
- Polymerization: Propylene monomers are linked together in a process catalyzed by Ziegler-Natta or metallocene catalysts. The polypropylene chemical structure (or pp structure) consists of a long carbon chain with a methyl group (CH₃) attached to every other carbon atom. The polypropylene repeat unit is C₃H6)n.
- Types: The arrangement of the methyl groups determines the three main types of PP polymers:
- Isotactic PP: Methyl groups are arranged on the same side of the chain (most common, highly crystalline).
- Syndiotactic PP: Methyl groups alternate sides of the chain (less common, high clarity).
- Atactic PP: Methyl groups are randomly arranged (amorphous, sticky, less useful).
Key Properties
pp material properties are a favorable balance of thermal, mechanical, and chemical attributes.
| Property | Value (Typical) | Significance |
| Melting Point | PP melting point (Tm) 160°C-170°C(pp melting temp) | Higher than PE, making it suitable for hot-fill containers (microwave-safe). |
| Density | Polypropylene density (pp density) 0.90 – 0.91 g/cm³ | Extremely low, making it the lightest major plastic; parts float in water. |
| Glass Transition Temp | Polypropylene Tg (pp glass transition temperature) -10°C to 0°C | Relatively low, but its semi-crystalline nature makes it useful over a broad PP temperature range. |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength, excellent resistance to fatigue. | High rigidity and resistance to repeated bending (perfect for living hinges). |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Resistant to most organic solvents, degreasing agents, and electrolytic attack. |
Applications and Uses
versatility of PP material leads to diverse PP applications:
- Packaging: PP packaging includes films, wraps, and containers for food, dairy, and pharmaceuticals.
- Consumer Goods: Housewares, appliances, toys, and luggage.
- Automotive: Interior trim, battery cases, bumpers, and fender liners.
- Textiles: Polypropylene fibers are used to make carpets, ropes, thermal clothing, and non-woven fabrics. Note: PP cotton or polypropylene cotton is a term for synthetic stuffing/wadding, not natural cotton.
- Medical: Disposable syringes, bottles, and laboratory equipment due to its ability to be steam-sterilized.

Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages (Why choose PP material) | Disadvantages |
| Low Cost | Poor UV resistance (requires stabilizers for outdoor use). |
| Lightest Major Plastic (Density is less than 1.0) | Susceptible to oxidation at high temperatures. |
| Excellent Chemical Resistance | Poor impact resistance at very low temperatures. |
| Exceptional Fatigue Resistance (Ideal for living hinges) | Difficult to bond (requires specialized glues or surface treatment). |
| Good Heat Resistance (High PP melt temp) |
Frequently Asked Questions
PP Screws, Nuts and Flat Washers
PP Cross counter sunk head screw
$1.00PP Cross pan head screw
$1.00PP Flat washer
$1.00PP Hex nut
$1.00PP Hexagon head bolt
$1.00PP Hexagon socket head screw
$1.00





