What is Polyvinylidene Fluoride(PVDF)??
Polyvinylidene Fluoride is an addition PVDF polymer synthesized through the PVDF polymerization of vinylidene fluoride (VDF), a highly durable and chemically resistant thermoplastic polymer that belongs to the fluoropolymer family. Often commercially recognized by the trade name Kynar, PVDF is prized for its exceptional balance of inertness, thermal stability, and mechanical strength.
The Structure and Composition of PVDF
Polyvinylidene Fluoride is an addition polymer derived from the vinylidene fluoride (VDF) monomer.
PVDF Polymerization and Structure
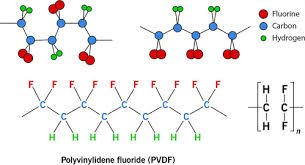
How is PVDF produced? The process involves the PVDF polymerization of VDF monomers (CH₂=CF₂). The resulting PVDF polymer has a simple and highly symmetric repeating unit.
- PVDF Structure: The structure of PVDF consists of a repeating unit with two carbon atoms, two hydrogen atoms, and two fluorine atoms, leading to the chemical formula (C₂H₂F₂)n. The fluorine atoms are highly electronegative and contribute significantly to the polymer’s unique properties.
- Contrast: It is crucial to distinguish PVDF from polyvinyl fluoride (PVF), which has a different chemical structure (CH₂=CHF monomer).
Key Polyvinylidene Fluoride Properties
The combination of the strong C–F bonds and the crystalline nature of PVDF results in an outstanding set of PVDF properties.
| Property | Description | Typical Value | Notes |
| Thermal Resistance | High continuous use temperature. | Up to 150°C | Remains stable under thermal stress. |
| PVDF Melting Point (Tm) | The temperature at which the crystalline structure melts. | 155°C to 177°C | Lower than PTFE, but sufficient for harsh environments. |
| Chemical Inertness | PVDF chemical resistance is excellent. | Resistant to most acids, bases, and halogens. | Ideal for use with aggressive chemicals. |
| Density | PVDF density (or density of PVDF) is high. | 1.75 – 1.90 g/cm³ | Heavier than most common plastics. |
| Special Electrical | Strong electrical response. | High PVDF dielectric constant and piezoelectric effect. | Used in transducers and capacitors. |
| UV Resistance | Excellent stability. | Highly resistant to UV light and weathering. | Maintains color and strength outdoors. |
Applications and Grades of PVDF
The superior properties of PVDF have made it indispensable across several industries.
- Chemical Processing: Due to its high chemical resistance, PVDF is used for piping, pumps, valves, and liners in chemical plants and semiconductor manufacturing.
- Batteries: Used as a binder in lithium-ion battery cathodes and in separators due to its electrochemical stability.
- Architectural Coatings: The Kynar PVDF or Arkema Kynar PVDF (from Arkema PVDF, a major manufacturer) forms the basis for long-life, weather-resistant exterior coatings.
- Membranes: Used to create microfiltration and ultrafiltration PVDF film for water treatment due to its hydrophobic properties.
- Specialty Filaments: Used for PVDF filament in 3D printing where chemical resistance and heat resistance are required.

Copolymers: PVDF-HFP
For specialized applications, PVDF is often copolymerized with hexafluoropropylene (HFP), creating PVDF-HFP (or PVDF HFP). This modification improves flexibility and processability while retaining many of the core PVDF properties, making it particularly useful in battery electrolytes and specialized membranes.
Advantages and Disadvantages of PVDF
| Advantages (Why choose PVDF plastic) | Disadvantages |
| Exceptional Chemical Resistance | High PVDF price compared to commodity plastics. |
| High Toughness and Abrasion Resistance | Lower maximum service temperature than PTFE. |
| Excellent Weatherability (UV and Oxidation) | Soluble in some highly polar solvents (e.g., ketones, DMF). |
| Good Processability (Can be melted and processed easily) | High density. |
| Unique Piezoelectric/Dielectric Properties |
Frequently Asked Questions
PVDF Screws, Nuts and Flat Washers
PVDF Cross counter sunk head screw
$1.00PVDF Cross pan head screw
$1.00PVDF Flat washer
$1.00PVDF Hex nut
$1.00PVDF Hexagon socket bolts
$1.00PVDF Hexagonal bolts
$1.00





